[C++/CLI]サブスレッドからフォームを操作する
2016/02/18
最近、ようやくWindowsプログラミングを始めました。
今回はJavaの時の様にいきなり無茶をしない様に気を付けています。
(始めてのJavaでいきなりMySQLを操作しようとしました、なんとか出来ました)
ウインドウ(フォーム)は中でループがぐ~るぐるなので止めちゃ行けないから、重たい処理やループでぐ~るぐるする物(イベントの監視とか)はサブスレッドにするらしいです。
ただ、他のスレッドのフォームを操作すると怒られちゃうので、BeginInvokeとデリゲートなるモノを用いて操作するのですが、それがググっても少しパッとしなかったのでメモも兼ねて記事にします。
スポンサーリンク
ウインドウは止められない!!
ご存知の方が大半だと思うのですが、念のために説明しておくと、
Windowsでのウインドウ(フォーム)はイベント駆動と呼ばれる手法で行っています。
簡単に説明すると、フォームが呼び出されると、内部でぐ~るぐるとループが回ってイベントの通知(ボタンがクリックされた、など)を待っており、イベントの通知があればそのイベントをキューに入れ、キューから関数を呼び出しています。
ですので、フォーム内で時間の掛かる処理を行ってしまうと、ボタンのクリックなどのイベントが応答できなくなり、いわゆる「応答なし」になる、と言う訳です。
(一般的に、0.1秒以上掛かるとアプリケーションの停止をユーザが認識出来るらしい)
サブスレッド
と言う訳で、ほぼ例外なく、その「時間のかかる処理」はサブスレッドに切り分けて行う事になるのですが、殆どの場合は「処理開始、終わり、完了!!」とはならないはずです。
「処理を開始します」、「処理を実行しています」、「処理が完了しました」、「処理の結果です」……と言った具合に、処理が実行されている事、完了した事をユーザに通知してやらねばなりません。
と言う訳で、通知してあげましょう「textBox1->AppendText("処理が完了しました!!");」とかやっちゃうと以下の様なエラーが出ます。
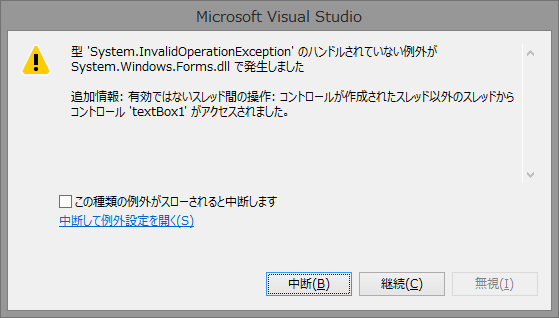
フォームの操作はスレッドセーフでは無いため、この様なエラーが発生します。
そこで登場するのがBeginInvokeとデリゲートです。
サブスレッドから操作
サブスレッドからフォーム上の要素を操作するためには「BeginInvoke」と言う物を使用します。
この、「BeginInvoke」は、最初の方で説明したイベントの通知が入る「キュー」に「この関数を呼び出してください」と言う命令を突っ込みます。
メインスレッドはループでぐ~るぐると回りながらキューを取り出していくため、「この関数を呼び出してください」と言う命令が取り出されて実行されます。
つまり、関数を呼び出す命令が「メインスレッド」で実行されるのです。
言い換えれば、サブスレッドからフォームを安全に操作しているのではなく、「メインスレッドにフォームの操作を行う関数の実行を依頼」しているのです。
呼び出される関数自体はメインスレッドで実行されているため、ここでSleep(9999);とかやったら当然ながらフリーズします。
実際にやってみる
と言っても、そう難しい物ではありません。
簡単なサンプルが以下の通りです。
// サブスレッド
private: System::Void subThread() {
// ここで何か重たい処理とか
Sleep(5000);
// BeginInvokeとデリゲート
BeginInvoke(gcnew sampleDele(this, &MyForm::execDele),"処理が完了しました!!");
}
// デリゲート
private: delegate System::Void sampleDele(String ^str);
// 呼び出される関数
private: System::Void execDele(String ^str) {
textBox1->AppendText(str);
}
これで分かる人は殆ど居ないと思うので解説すると
まず最初に、以下の様にしてフォームの要素を操作する関数と、デリゲートを定義します。
// デリゲート
private: delegate System::Void sampleDele(String ^str);
// 呼び出される関数
private: System::Void execDele(String ^str) {
// ここが処理部
textBox1->AppendText(str);
}
次に、サブスレッド側からBeginInvokeの引数としてデリゲートを渡す、と言う訳です。
BeginInvoke(gcnew sampleDele(this, &クラス名::execDele),"処理が完了しました!!");
基本的にこれだけなのでこれ以上の解説が逆に難しいのですが、この様にすることでサブスレッドからフォームの要素を操作する事が出来ます。
サンプル
「解説が意味わかんねぇよクソッタレ」と言う方のために、実際の利用例を用意しました、参考にしてみて下さい。
VisualStudio 2015 Communityでの動作を確認しました。
#pragma once
#include <windows.h>
// ここを変更すると進捗状況バーの速度が変わります。
#define SLEEP_TIME 150
namespace Sample {
using namespace System;
using namespace System::ComponentModel;
using namespace System::Collections;
using namespace System::Windows::Forms;
using namespace System::Data;
using namespace System::Drawing;
using namespace System::Threading;
/// <summary>
/// MyForm の概要
/// </summary>
public ref class MyForm : public System::Windows::Forms::Form
{
public:
MyForm(void)
{
InitializeComponent();
//
//TODO: ここにコンストラクター コードを追加します
//
}
protected:
/// <summary>
/// 使用中のリソースをすべてクリーンアップします。
/// </summary>
~MyForm()
{
if (components)
{
delete components;
}
// スレッドが安全に停止する様にですね……
m_stop = true;
}
private: System::Windows::Forms::ProgressBar^ progressBar1;
private: System::Windows::Forms::Button^ button1;
private: System::Windows::Forms::TextBox^ textBox1;
protected:
private:
/// <summary>
/// 必要なデザイナー変数です。
/// </summary>
System::ComponentModel::Container ^components;
#pragma region Windows Form Designer generated code
/// <summary>
/// デザイナー サポートに必要なメソッドです。このメソッドの内容を
/// コード エディターで変更しないでください。
/// </summary>
void InitializeComponent(void)
{
this->progressBar1 = (gcnew System::Windows::Forms::ProgressBar());
this->button1 = (gcnew System::Windows::Forms::Button());
this->textBox1 = (gcnew System::Windows::Forms::TextBox());
this->SuspendLayout();
//
// progressBar1
//
this->progressBar1->Location = System::Drawing::Point(13, 198);
this->progressBar1->Name = L"progressBar1";
this->progressBar1->Size = System::Drawing::Size(259, 22);
this->progressBar1->TabIndex = 0;
//
// button1
//
this->button1->Location = System::Drawing::Point(197, 226);
this->button1->Name = L"button1";
this->button1->Size = System::Drawing::Size(75, 23);
this->button1->TabIndex = 1;
this->button1->Text = L"開始";
this->button1->UseVisualStyleBackColor = true;
this->button1->Click += gcnew System::EventHandler(this, &MyForm::button1_Click);
//
// textBox1
//
this->textBox1->Location = System::Drawing::Point(13, 13);
this->textBox1->Multiline = true;
this->textBox1->Name = L"textBox1";
this->textBox1->ReadOnly = true;
this->textBox1->Size = System::Drawing::Size(259, 179);
this->textBox1->TabIndex = 2;
//
// MyForm
//
this->AutoScaleDimensions = System::Drawing::SizeF(6, 12);
this->AutoScaleMode = System::Windows::Forms::AutoScaleMode::Font;
this->ClientSize = System::Drawing::Size(284, 261);
this->Controls->Add(this->textBox1);
this->Controls->Add(this->button1);
this->Controls->Add(this->progressBar1);
this->Name = L"MyForm";
this->Text = L"Sample for jyn.jp";
this->ResumeLayout(false);
this->PerformLayout();
}
#pragma endregion
// スレッドスイッチ
bool m_stop = false;
// ボタンクリック
private: System::Void button1_Click(System::Object^ sender, System::EventArgs^ e) {
// ボタンを無効化する
button1->Enabled = false;
// 進捗状況をリセット
progressBar1->Value = 0;
// スレッドを用意
Thread ^progressThread = gcnew Thread(
gcnew ThreadStart(this, &MyForm::subThread)
);
// バックグラウンド処理
progressThread->IsBackground = true;
// スレッドを開始
progressThread->Start();
}
// サブスレッド
private: System::Void subThread() {
// ここで何か重たい処理とか
for (int i = 1; i < 101; ++i) {
// フォームが終了されてたらこのスレッドも終了
if (m_stop) {
return;
}
// 重たい処理を再現
Sleep(SLEEP_TIME);
// デリゲートの実行
BeginInvoke(
gcnew sampleDele(this, &MyForm::execDele),
(i.ToString() + "\n"),
i
);
}
// 2つめのデリゲート
BeginInvoke(gcnew sampleDele2(this, &MyForm::enableButton));
}
// デリゲート
private: delegate System::Void sampleDele(String ^str, int count);
private: System::Void execDele(String ^str, int count) {
progressBar1->Value = count;
textBox1->AppendText(str);
}
// デリゲート2
private: delegate System::Void sampleDele2();
private: System::Void enableButton() {
button1->Enabled = true;
}
};
}